 Français
Français Antibiotic Drugs
Telavancin
It is an antibiotic belonging to the class of lipoglycopeptide drugs. It is a semisynthetic derivative of vancomycin.
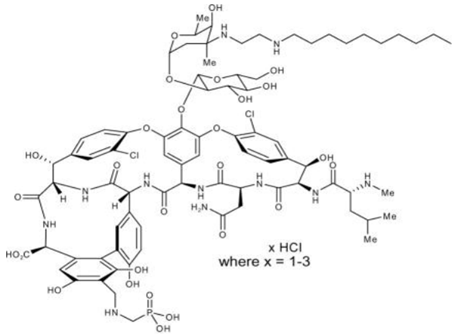
Chemical structure
The chemical formula is C80H106C12N11O27P • xHCl (where x = 1-3) and MW is 1755.6
Mechanism of action
Telavancin is bactericidal drug acts by inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Deficient cell wall results in swelling of bacteria and finally death.
Pharmacokinetics
Telavancin is given by intravenous route. Its long duration of action permits its once daily dosing.
Antimicrobial spectrum
Telavancin is active against gram-positive bacteria but does not have clinically significant activity against gram-negative bacteria. It may be active against Actinomyces species, Clostridium difficile and some anaerobic bacteria. Some vancomycin-resistant enterococci have decreased susceptibility to telavancin.
Indications and uses
Telavancin is used for treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections. It is also indicated for treatment of certain other infections caused by gram-positive bacteria. If recognized or presumed pathogens include gram-negative or anaerobic bacteria, concurrent use of other antibiotics is indicated.
Administration and dosage
Adults
| Condition | Dosage (IV) |
| Skin and Skin Structure Infections | 10 mg/kg/day for 7–14 days. |
It is administered by i.v. infusion over 60 minutes.
Duration of therapy should be based on severity and location of infection and patient's clinical and bacteriologic response
Precautions, contraindications and warnings
Telavancin interferes with PT, INR, aPTT, activated clotting time, and tests based on factor Xa. Telavancin should be given cautiously in patients of pre-existing renal disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, CHF. Telavancin is contraindicated in pregnancy, patients with QTc prolongation.
Adverse effects
Side effects of telavancin are taste disturbance, nausea, vomiting, constipation, decreased appetite, dizziness, headache, insomnia, pruritus, rash, rigors, infusion site pain and erythema.
Technical Description on Telavancin
It is an antibiotic belonging to the class of lipoglycopeptide drugs. It is semi-synthetically derived from vancomycin.
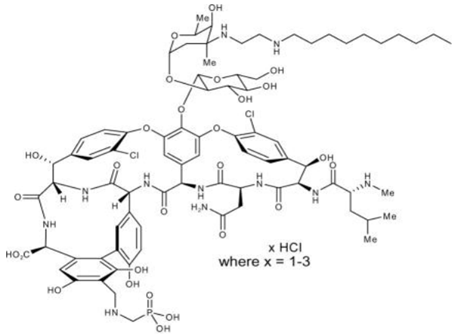
Chemical structure
Telavancin is structurally identical to the glycopeptides but has extra moieties which are have hydrophilic and hydrophobic property.
The chemical formula is C80H106C12N11O27P • xHCl (where x = 1-3) and MW is 1755.6
Preparations available
For IV use - 250 mg and 750 mg/vial
Mechanism of action
Telavancin is bactericidal in action and known to act through two mechanisms:
- Like Vancomycin, it attaches specifically and non-covalently to the terminal D-Ala-D-Ala stem peptides of the strands of glycan which are not linked in a criss cross manner. This leads to inhibition of the polymer formation of the peptidoglycan layer and also affects the steps involved in cross linking of the layers. Finally the formation of the cell membrane is disrupted.
- Secondly the other mechanism is based on the collaboration of the lipid bilayer plasma membrane of the bacteria with the decylaminoethyl part of telavancin which has high lipophilicity. This leads to membrane of the bacteria being depolarized and ultimately leading to damage to the part of the cell membrane involved in maintaining the integrity of the cell.
Microbiology
It is active against:
- Staphylococcus aureus (including MRSA)
- Staphylococcus haemolyticus and epidermidis
- Streptococcus pyogenes (group A β-hemolytic streptococci)
- S. agalactiae (group B streptococci)
- Streptococcus dysgalactaie
- S. anginosus group
- Enterococcus faecalis and faecium (vancomycin-sensitive strains only)
Telavancin does not have clinically significant activity against gram-negative bacteria. It may be active against Actinomyces species, Clostridium difficile and some anaerobic bacteria.
Some strains of enterococci which are resistant to vancomycin are not sensitive to telavancin.
Resistance
There are no resistant mutant strains with telavancin as seen in a particular study assessing various strains of staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci which were resistant to multiple drugs.
Telavancin does not exhibit any cross resistance to antibacterial agents of other class.
Pharmacokinetics
After i.v. infusion, telavancin has a short distribution phase and is dispersed into the central and peripheral compartments. Half-life is about 8 hours in adults. It is about 90% bound to plasma proteins and it is unaltered in liver or kidney dysfunction. There are no known telavancin metabolites. The CYP 450 enzyme isoforms like CYP 1A2, 3A4, 3A5, 4A11, 2C9, 2D62 and C19 are not involved in the metabolism of telavancin. Thus any the drugs which inhibit or induce the above mentioned enzymes do not affect the metabolism of telavancin. The major route of excretion of telavancin is through the kidney. The exact mechanism of metabolism of telavancin is unknown.
Therapeutic Uses
- Infections of the skin and appendages
It is indicated for the therapy of infections of the skin and appendages which are complicated caused by sensitive bacteria.
- It is also indicated for the therapy of certain other infections due to gram-positive bacteria.
Dosage (Adults)
| Condition | Dosage (IV) |
| Infections of skin and appendages | 10 mg/kg/day for 1-2 weeks |
It is administered by i.v. infusion over 60 minutes.
Drug Interactions
Telavancin shows in vitro evidence of synergistic antibacterial effects with gentamicin.
Telavancin also shows in vitro evidence of synergistic antibacterial effects against MRSA with rifampicin, cefepime, meropenem, ceftriaxone, and ciprofloxacin.
Laboratory interactions
If blood samples are drawn 0–18 hours after a dose of Telavancin, it interferes with Prothrombin Time, INR, aPTT, activated clotting time, and tests based on factor Xa.
Telavancin also interferes with urine qualitative and Quantative protein assays which are performed by dipstick method.
Special Populations
- Elderly Patients
Telavancin is less effective in persons who are greater than 65 years of age.
- Liver dysfunction
Dosage alteration is not required in adults with mild or moderate liver dysfunction.
- Kidney dysfunction
Dose must be modified in patients with kidney dysfunction.
- Pregnancy
It is pregnancy category C drug.
- Lactation
Caution is advised as it not known whether telavancin is secreted during lactation.
- Children
The efficacy and safety parameters have not been studied in children or adolescents aged less than 18 years.
Warnings and Precautions
- Kidney toxicity
Impaired kidney function has been seen in patients receiving telavancin.
Renal function tests are advised prior to initiation of Telavancin and every 2 to 3 days during therapy and more often if indicated, and at end of therapy.
- Teratogenic effect or Neonatal Morbidity
Animal studies have shown some developmental defect with telavancin, hence it should not be used in pregnancy and also contraception is advised to prevent pregnancy during treatment.
- Reactions due to infusion
If telavancin is administered rapidly IV it can result in a reaction known as the “Red-man syndrome.” This reaction is manifested by flushing of the upper body, increased itching urticaria, pruritus, or skin rashes.
Telavancin should be slowly infused over a period of one hour to avoid such reactions and unfortunately if such a reaction occurs the rate of infusion should be further slowed or it should be stopped.
- Clostridium difficile-associated enterocolitis
There is a risk of development of enterocolitis due to clostridium difficile. Also super-infections can develop due to modification of the intestinal flora due to telavancin.
- CVS Effects
Telavancin can lead to prolongation of the QTc interval.
Carcinogenic potential, Mutagenic potential and impaired fertility
Animal studies have not proved any of these with telavancin.
Adverse Effects
The common adverse effects observed were:
- Altered taste sensations, constipation, nausea
- Anorexia, Foamy urine
- Skin rashes and generalized pruritus
- Pain at the infusion site, rigors, and erythema
- Giddiness, decreased sleep, headache