 Français
Français Antibiotic Drugs
Daptomycin
Daptomycin is a novel antibiotic first in the class of drugs known as lipopeptide.
Chemical structure
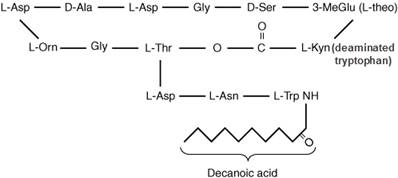
The chemical formula is C72H101N17026 and MW is 1620.27. The chemical structure is:
Mechanism of action
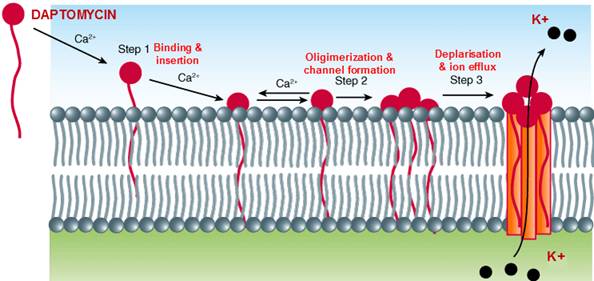
Through step 1, step 2 and step 3 daptomycin causes inhibition of DNA, RNA and protein synthesis and breakdown of organism resulting in cell death.
Pharmacokinetics
Daptomycin is poorly absorbed orally and should only be administered intravenously. Intramuscular injection is prohibited as it causes direct toxicity.
Antimicrobial spectrum
Daptomycin is a bactericidal antibiotic selectively active against aerobic, facultative, and anaerobic gram-positive bacteria Gram-positive aerobes. Daptomycin is inherently inactive against gram-negative bacteria as they possess an outer membrane that the drug is incapable to penetrate and they lack specific factors essential for its activity.
Indications and uses
Daptomycin is indicated for treatment of complicated skin and soft tissue infections, complicated bacteremia and right-sided endocarditis. Its efficacy was equivalent to that of vancomycin or semisynthetic penicillins. Daptomycin was found to be inferior in comparison to other drugs for treatment of community-acquired pneumonia, most probably due to its inactivation in pulmonary surfactant, and hence it should not be used for this indication.
Administration and dosage
Adults
| Condition | Dosage (IV) |
| Skin and Skin Structure Infections | 4 mg/kg/day for 7–14 days |
| Complicated Infections | 4 mg/kg/day for 7–14 days |
| Bacteremia | 6 mg/kg/day for at least 2–6 weeks. |
Do not administer more frequently than once daily. Higher doses up to 10-12 mg/kg/day are well tolerated and may be used accordingly.
Precautions, contraindications and warnings
It is advised that serum CK concentrations should be measured weekly during daptomycin treatment and more frequently in those treated concurrently with statins.
Adverse effects
Side effects of daptomycin are constipation, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, headache, insomnia, dizziness, anxiety, rash, pruritus, abnormal liver function test results, CK elevations, renal failure, anemia, dyspnea, fever.
Technical Description on Daptomycin
Daptomycin is a novel antibiotic first in the class of drugs known as lipopeptide. It is a cyclic lipopeptide derived from Streptomyces roseosporus.
Chemical structure
Daptomycin is a cyclic lipopeptide compound with 13 amino acids and which comprises of a core with hydrophilic properties and also a tail which has high lipophilicity. The chemical formula is C72H101N17026 and MW is 1620.27. The chemical structure is:

Preparations available
Parenteral: 0.25 or 0.5 g lyophilized powder to reconstitute for IV injection
Mechanism of action

Step 1: Attachment of daptomycin takes place with the help of calcium ion and then the tail with high lipophilicity is inserted into the plasma membrane of the gram positive bacteria.
Step 2: Channel is constitutively formed followed by depolarisation.
Step 3: Due to depolarisation there is ion leakage (mainly potassium) leading to inhibition of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis and breakdown of organism resulting in cell death.
Antimicrobial activity
Daptomycin is a bactericidal antibiotic selectively active against aerobic, facultative, and anaerobic gram-positive bacteria Gram-positive aerobes:
- Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only)
- Staphylococcus aureus (including MRSA)
- Glycopeptide-intermediate S. aureus (GISA)
- Penicillin-resistant pneumococci
- S. agalactiae (group B streptococci)
- Streptococcus dysgalactiae
- Streptococcus pyogenes (group A β-hemolytic streptococci)
- Corynebacterium jeikeium
- Vancomycin resistant and sensitive enterococcus faecalis
- Vancomycin resistant and sensitive enterococcus faecium
- Staphylococcus epidermidis and haemolyticus
- Clostridium difficile and perfringens,
- Propionibacterium
- Peptostreptococci
Daptomycin is inherently inactive against gram-negative bacteria as they possess an outer membrane that the drug is incapable to penetrate, and they lack specific factors essential for its activity.
Resistance
Mechanisms of resistance to daptomycin have not been fully categorized. Genetic changes in the mprF gene (regulating cell membrane charge) correlating to daptomycin resistance have been suggested. In vitro emergence of bacterial resistance most commonly occurs by spontaneous mutations, serial passage, or chemical mutagenesis.
Pharmacokinetics
Daptomycin is poorly absorbed orally and should only be administered intravenously. Intramuscular injection is prohibited as it causes direct toxicity. Protein binding is 90-93% mainly to albumin. The serum t1/2 is 8-9 hours. Even though it has good penetration in the lungs, it is inactivated by pulmonary surfactant. In vitro studies specify that daptomycin is not metabolized by CYP isoenzymes. Inactive metabolites have been detected in urine. Approximately 78-80% of the administered dose is recovered in urine; and about 6% is excreted in faeces. Dosage adjustment is necessary for creatinine clearance <30 mL/ minute; which is done by administering the recommended dose every 48 hours. In patients undergoing haemodialysis, dose should be administered instantly after dialysis.
Therapeutic uses
Daptomycin is indicated for treatment of:
- Infections of the skin and appendages (complicated) caused by susceptible organisms.
- Complicated bacteraemia and right-sided endocarditis. The efficacy of daptomycin is equal to that of semisynthetic penicillins or vancomycin.
- Daptomycin was found to be inferior in comparison to other drugs for treatment of community-acquired pneumonia, most probably due to its inactivation in pulmonary surfactant, and hence it should not be used for this indication.
Dosage (Adults)
| Condition | Dosage (IV) |
| Infections of skin and its appendages | 4 mg/kg/day for 1-2 weeks |
| Complicated Infections | 4 mg/kg/day for 1-2 weeks |
| Bacteraemia | 6 mg/kg/day for a minimal period of 2–6 weeks. |
Special populations
- Kidney dysfunction
Dose alterations are required in persons with kidney dysfunction according to the levels of creatine clearance.
- Liver dysfunction
In patients with mild or moderate liver dysfunction there is no need to change the dose.
- Elderly patients
The efficacy was less in elderly population in clinical trials and also the risk of side effects was more.
- Pregnancy
Animal studies have not proved any teratogenic effect due to Daptomycin.
- Lactation
Data is not available about its secretion during lactation.
- Children
The efficacy and safety of Daptomycin has not been studied in population less than 18 years of age.
Drug Interactions
- Beta-Lactam antibiotics
There is evidence from some invitro studies that daptomycin along with penicillins or cephalosporins can exert synergism in killing bacteria like enterococci and staphylococci.
- HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins)
There is increased risk of muscular pain and weakness if daptomycin is prescribed along with statins.
- Rifampicin
There is evidence from some invitro studies that daptomycin along with rifampicin can exert synergism in killing bacteria like enterococci and staphylococci.
- Aminoglycosides
There is evidence from some invitro studies that daptomycin along with aminoglycosides like tobramycin or gentamicin can exert synergism in killing bacteria like enterococci and staphylococci.
- Daptomycin does not affect enzymes of the P450 system.
Contraindications
It is contraindicated if there is a prior history of hypersensitive reactions because of daptomycin.
Warnings
- Clostridium difficile-associated enterocolitis
There is a risk of development of enterocolitis due to clostridium difficile. Also super-infections can develop due to modification of the intestinal flora due to Daptomycin.
- Central and peripheral nervous system
Rarely signs and symptoms of neuropathy of cranial nerves or peripheral neuropathy have been seen.
- Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Treatment with Daptomycin can lead to development of eosinophilic pneumonia, but it is reversible with stoppage of therapy.
- Muscle and skeletal system
If Daptomycin is prescribed greater than a single dose per day it can lead to raised levels of creatine kinase (CK) in the serum. So frequent measurements of its levels are advised particularly if prescribed simultaneously with statins.
- There can be a failure of response to infection caused by staphylococcus aureus.
Carcinogenic potential, Mutagenic potential and impaired fertility
Animal studies have not proved any of these with daptomycin.
Adverse Reactions
- Loose stools or sometimes constipation, pain in abdomen, dyspepsia, vomiting
- Increased risk of infections due to bacteria and fungi
- Kidney failure, pyrexia, breathlessness, anemia
- Muscular pain and pain in the back
- Fluid accumulation in the pleural cavity
- Increased blood pressure, increased or decreased potassium levels in the serum, sometimes decreased blood pressure
- Giddiness, decreased sleep, anxious behaviour, headache
- Skin rashes, increased itching, deranged hepatic enzyme levels
- Generalized oedema, decreased body movements