 Français
Français Antibiotic Drugs
Ertapenem
Ertapenem sodium is a synthetic, parenteral carbapenem antibiotic.
Chemical structure
The empirical formula is C22H24N3O7SNa and MW is 497.50.The chemical structure is:
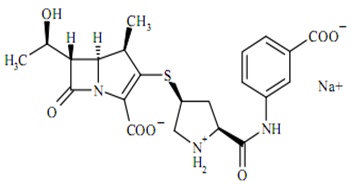
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of ertapenem is similar to beta- lactam antibiotics. The bactericidal action of ertapenem is due to the inhibition of cell wall synthesis leading to death of bacteria.
Pharmacokinetics
After intramuscular administration peak plasma concentrations are reached in approximately 2 hours.
Antimicrobial spectrum
Ertapenem is active against wide range of gram-positive, gram negative and anaerobic bacteria. Ertapenem is stable against hydrolysis by a number of beta-lactamases, including penicillinases, and cephalosporinases and extended spectrum beta-lactamases.
Indication, administration and dosage
| Condition | Daily Dose (IV or IM) Adults and Paediatric Patients >13 years of age | Daily Dose (IV or IM) Paediatric Patients 3 months to 12 years of age | Duration of treatment |
| Complicated intra-abdominal infections | 1 g | 15 mg/kg twice daily‡ |
5 to 14 days |
| Complicated skin and skin structure infections, including diabetic foot infections |
1 g | 15 mg/kg twice daily‡ |
5 to 14 days |
| Community acquired pneumonia | 1 g | 15 mg/kg twice daily‡ |
10 to 14 days |
| Complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis | 1 g | 15 mg/kg twice daily‡ |
10 to 14 days# |
| Acute pelvic infections including postpartum endomyometritis, septic abortion and post-surgical gynecologic infections |
1 g | 15 mg/kg twice daily‡ |
3 to 10 days |
- Dose should not to exceed 1 g/day in paediatric patients of 3 months to 12 years of age.
- Adult patients with diabetic foot infections should receive treatment up to 28 days of treatment.
- The duration of treatment in community acquired pneumonia and complicated urinary tract infections including pyelonephritis include a likely switch to a suitable oral therapy, after at least 3 days of parenteral therapy, once clinical improvement has been confirmed.
Prophylactic Regimen in Adults
| Indication | Daily Dose (IV) –Adults | Duration of treatment |
| Prophylaxis of surgical site infection following elective colorectal surgery | 1 g | Single IV dose given 1 hour prior to surgical incision |
Precautions, contraindicationa and warnings
Ertapenem is contraindicated in patients with prior history of hypersensitivity to any other drugs in the same class or to beta-lactams. Ertapenem is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to local anesthetics of the amide type as lidocaine HCl is used as a diluent for Ertapenem.
Adverse effects
Common side effects of ertapenem are infused vein complication, swelling, fever, abdominal pain, hypotension, constipation, diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, altered status, dizziness, headache, insomnia, dyspnea, pruritis, rash, vaginitis.
Technical Description on Ertapenem
Ertapenem sodium is a synthetically derived, parenteral carbapenem antibiotic.
Chemical structure
Ertapenem is a 1-beta methyl-carbapenem which is chemically similar to beta lactams. Its molecular formula is C22H24N3O7SNa and MW is 497.50.The chemical structure is:
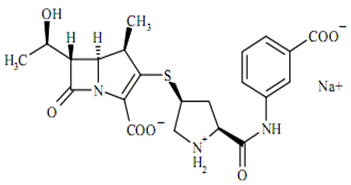
Preparations available
1 g ertapenem/vial for Intravenous or Intramuscular Use
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of ertapenem is similar to beta- lactam antibiotics. The bactericidal action of ertapenem is due to the inhibition of synthesis of the bacterial cell wall and is facilitated by the attachment of ertapenem to penicillin binding proteins.
Microbiology
Ertapenem is active against:
Gram positive bacteria
- Staphylococcus aureus which are sensitive to methicillin
- Streptococcus pyogenes and agalactiae
- Pneumococci which are sensitive to penicillin
Gram-negative bacteria
- E. coli
- Proteus mirabilis
- Haemophilus influenzae which do not produce beta lactamase
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
Anaerobic bacteria:
- Bacteroides fragilis, ovatus, distasonis, thetaiotaomicron and uniformis
- Clostridium clostridioforme
- Eubacterium lentum
- Porphyromonas asaccharolytica
- Prevotella bivia
- Peptostreptococcus
Resistance
A varied number of beta lactamases do not cause much hydrolysis of ertapenem but it undergoes hydrolysis by the metallo beta-lactamases. In vitro studies have reported that the key forms of resistance to ertapenem in gram-negative bacilli, is due to combinations of decreased accumulation which is both because of increased influx and decreased influx and beta lactamase hydrolysis.
There is a possibility of cross-resistance between ertapenem and other carbapenems, but in vitro studies and surveillance studies designate that it is not complete. As β-lactams do not share mutual mechanisms of actions with non-β-lactam antimicrobials, there is no probability of target-based cross-resistance between them.
Pharmacokinetics
After intramuscular administration, the bioavailability is 90-92%. Mean peak plasma concentrations are reached in approximately 2 hours Protein binding is about 85% to 95%.Ertapenem is eliminated predominantly by the kidneys. The main metabolite of ertapenem is the bacteriologically inactive. Dehydropeptidase-1 catalyzes the metabolism of ertapenem. Approximately 80% excreted in urine and ten per cent in faeces.
The t1/2 of ertapenem ranges from 2.5 to 4 hours.
Ertapenem does not inhibit metabolism mediated by any of the six major cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms.
Therapeutic uses
Ertapenem is indicated in the following conditions:
- Intra-abdominal infections (complicated) caused by sensitive organisms as mentioned above.
- Infections of skin and appendages (complicated) infections caused by sensitive organisms as mentioned above.
- Community-acquired pneumonia caused by pneumococci, H. influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis.
- Urinary system infection (complicated) caused by sensitive organisms like proteus, E.coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
- Acute pelvic infections
Dosage
| Condition | Dose/day Adults and children aged >13 years (Intramuscular or IV) | Dose/day Children aged 3 months-12 years (Intramuscular or IV) | Duration of treatment |
| Infections of intra-abdominal origin and Infections of the skin and appendages (complicated) | 1 g | 15 mg/kg/BD | 5 days to 2 weeks |
| Infections of urinary system (complicated) and Community acquired pneumonia | 1 g | 15 mg/kg/BD | 10 days to 2 weeks |
| Acute pelvic infections | 1 g | 15 mg/kg/BD | Three to ten days |
- A dose of greater than 1 gram per day should not be given in children aged 3 months to 12 years.
- Persons with diabetes and having foot infections should receive treatment up to 4 weeks.
For prophylaxis
A single dose of 1 g can be given by the intravenous route for prophylactic use in elective surgeries.
Drug interactions
- Probenecid
Simultaneous prescription of ertapenem and probenecid is not advised as probenecid causes inhibition of tubular secretion of ertapenem.
- Valproic Acid
Ertapenem decreases the plasma levels of valproic acid.
Special populations
- Kidney dysfunction
Modifications in dose are required in persons with kidney dysfunction.
- Liver dysfunction
Not much data is available about the effect of liver dysfunction on the metabolism of ertapenem.
- Patients on Haemodialysis
An extra dose of 150 mg should be given after haemodialysis.
- Pregnancy
It is a pregnancy Category B drug.
Ertapenem penetrates the placental barrier in rats and can cross the human placenta. No clinical trials have been conducted studying the teratogenic effects of ertapenem.
- Lactation
Ertapenem is secreted during lactation.
- Children
As no clinical data is available, ertapenem should not be prescribed in infants below three months of age.
As CSF penetration is poor, it should not be prescribed for the treatment of meningitis in the paediatric population.
Precautions
- Hypersensitivity Reactions
Like other beta-lactam antibiotics serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitive reactions can occur with Ertapenem.
- Convulsions
Convulsions and other CNS adverse effects have been seen with Ertapenem.
- Clostridium difficile-Associated enterocolitis
Like other antibiotics, it can also be seen with ertapenem.
Contraindications
- Ertapenem is contraindicated in persons with prior history of hypersensitive reaction to any of the beta-lactams or any other drug.
- Ertapenem is contraindicated in individuals with a known hypersensitive reaction to Amide local anaesthetics as lidocaine hydrochloride is used as a diluent for Ertapenem.
Carcinogenic, Mutagenic potential, and impaired fertility
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in animals have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of ertapenem. However, neither mutagenic nor carcinogenic potential nor impairment of fertility was found in a number of tests conducted in selected animals.
Adverse reactions
The common adverse effects are:
- Pain in the abdomen, Oedema, pyrexia
- Venous complications due to infusion
- Fall in blood pressure
- Decreased sleep, giddiness, headache and altered mental status
- Skin rashes, breathlessness, vaginal inflammation, increased itching
- Loose stools sometimes constipation, vomiting
Other adverse effects rarely seen are:
- Distension of the abdomen, pain in the abdomen, oedema of the face, septicaemia, dehydration, decreased body movements, candidiasis, weight loss, pain at the injection site, extravasation of drug, thrombophlebitis
- Increased blood pressure, cardiac failure, Increased heart rate, arrhythmias
- Acid reflux, candidial infection of oral cavity, bleeding in the GIT,decreased appetite, difficulty in swallowing, cholelithiasis, altered taste
- Pain in the extremities
- Convulsions, anxious behaviour, depression, vertigo parasthesia
- Recurrent cough, fluid accumulation in pleural cavity, blood in sputum, hypoxemia, bronchoconstriction
- Kidney dysfunction, candidial infection of vagina, blood in urine, urinary retention